Stellar Mass
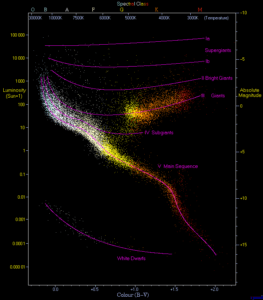
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram – By Richard Powell – The Hertzsprung Russell Diagram, CC BY-SA 2.5, Link
The next mystery to be addressed by astronomy concerned stellar mass. Henry Russel proposed in 1914 that the hotter, more luminous stars had greater mass, while the cooler stars had a lower mass. This means that the stars on the upper left of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram had a greater stellar mass and had a blue color, while those on the lower right corner of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram were red stars with much lower masses. Unfortunately, early in the twentieth century, there was no way astronomers could measure stellar mass.
How astronomers figured this out represents one of the greatest accomplishments in astrophysics of the twentieth century.
The Doppler Effect
Most of us who have lived around railroads understand that the train’s horn will go to a lower pitch when a train passes by. This is not because the train’s conductor changes the pitch but because the sound waves become “stretched” as the speeding train passes. This lengthens the sound wave and causes it to have a lower frequency producing a lower sound.
It is also possible to determine the speed at which the train moves toward or away from us by changing the sound pitch. For example, if the train moves very quickly away from us, the pitch becomes lower than if the train moves away more slowly.
A similar thing happens with stars. When they move toward us, the star becomes “blue-shifted,” while the stars moving away from us become “red-shifted.” Thus, it is possible to determine the speed at which the star moves away from us by knowing the extent of the redshift.
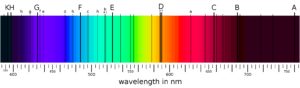
Fraunhofer Lines – By Fraunhofer_lines.jpg: nl:Gebruiker:MaureenV< Link
The redshift itself is measured by looking at those absorption lines in a stellar spectrogram; different elements within the star produce the lines. The normal position of these lines is known by experimentation with various elements on Earth. Still, when a star moves farther away, the entire spectrum is shifted toward the red area of the spectrum. The amount of this shift is determined by the velocity at which the star moves away from the Earth.
Measuring Stellar Mass through Radial Velocity
Imagine viewing the Earth as it rotates around the Sun. Observation of this motion from the side would show the earth moving away from us during half its orbit while moving toward us during the second half of its orbit. There would be times when the earth appeared to stand still when it transitioned from moving away from us to moving toward us. The Earth never really changes speed in its orbit around the Sun, but it appears to when viewing from the side.
Using this principle, it is possible to measure the mass of stars. This is how.
Kepler’s third law of motion states that the square of the orbital period (the number of years it takes for a planet to orbit the Sun) equals the cube of the semi-major axis of its elliptical orbit. Several decades later, Newton was able to include the masses of the Sun and Earth within this formula and to generalize to two stars moving around each other:
D3=(M1+M2)P2
Where D is the semi-major axis of the orbit, P is the number of years for two stars to rotate about each other, and M1 and M2 represent the masses of the two stars.
This means if you know the time required for one star to rotate around another and can measure the orbit’s semi-major axis, you can determine the sum of the masses of the two stars!
The problem was this derivation gives the sum of the masses of the two stars and does not give the mass of an individual star.
Astronomers throughout the nineteenth century figured all of this out and were anxious to find binary stars to try to calculate their masses. To do this calculation, astronomers needed to know,
- the distance of the binary star system (to convert the angular separation between them into a real distance),
- the time for the stars to rotate around each other.
Only a few such systems were close enough to Earth to make these delicate observations.
Finding the Binary Stars To Make Calculations of Stellar Masses

By www.robertaitken.net, Original uploader was Dr8 at en.wikipedia – Transferred from en.wikipedia, Public Domain, Link
Some astronomers specialized in finding binary star systems whose measurements could be made with some degree of accuracy. One such astronomer was Robert Grant Aitken, who worked at the Lick Observatory. He was very successful in finding these stars, and by 1915 he had discovered 3100 new binary stars.
This is nice, but it still does not help measure individual stars’ mass in a binary system.
The measurement of individual stars becomes possible when observing an “eclipsing binary system.” An eclipsing binary system is viewed from the side so that the stars appear to alternate, moving toward you and moving away from you. This allows astronomers to measure the ratio of the two masses! If they are of equal mass, their radial velocities away and toward the observer will be equal. Thus, the inequality of the radial velocities is proportional to their difference in mass.
The problem was that only a few binary star systems were discovered whose stars were seen from the side. For example, in 1910, only nine such systems were discovered, but by 1917 this list grew to 113.
The amazing discovery of all this work was that the more massive stars were the brightest with the greatest surface temperatures – the blue stars.
Astronomers broke the code for the dwarf stars. The more massive a star, the hotter and brighter the star. The means that the location of a dwarf star on the HR diagram is controlled by only one parameter – the star’s mass.
Arthur Eddington was then able to make a formula relating the mass of a star to its brightness. The Eddington equation was,
the luminosity of a main-sequence star is proportional to its mass raised to 3.5 power.
The relationship shows that the luminosity of a star – its absolute brightness – radically increases as its mass increases. So, for example, a star that has twice the mass of the Sun has about eleven times the Sun’s brightness.
The Real Importance of Stellar Mass Determination
The real importance of the inter-relationship between mass, luminosity, and surface temperature now becomes clear. The real importance was realizing that if you know the star’s spectral type (blue, red, yellow, etc.), you know the surface temperature and can place the star on the HR main sequence diagram. When this is done, you then know its absolute brightness.
If you know the absolute brightness of a star and the apparent brightness, you can now calculate the distance to a star!
No matter where the star is in the universe, if its spectral type and apparent brightness are known, then you can measure how far away it is. This is truly amazing.
The Real Problem
The main problem with this approach is how do you know whether a star is on the main sequence – or not. For example, some red stars are off the main sequence to the upper right, while some white stars are off the main sequence to the lower left.
This was a problem solved by an unlikely source – star clusters.




